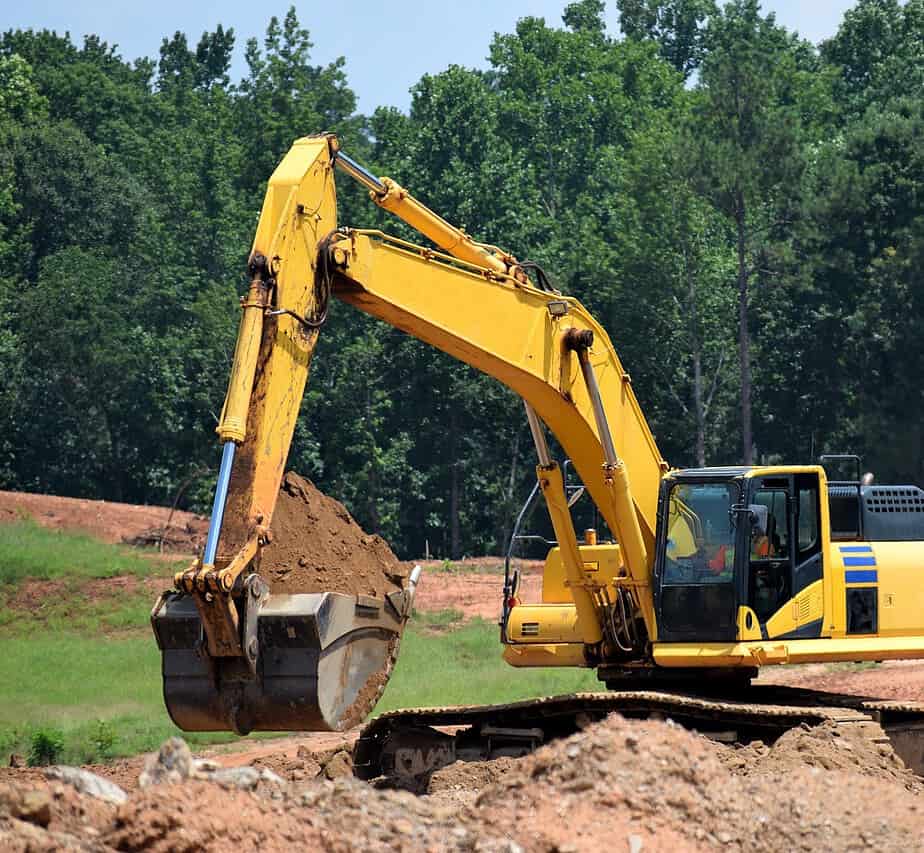
Introduction
Farm dams play a crucial role in agricultural operations, providing water storage for irrigation, livestock, and domestic use. However, like any other infrastructure, they require regular maintenance to ensure their longevity and optimal functionality. Neglecting proper maintenance practices can lead to a host of problems, such as structural damage, water quality issues, and decreased water storage capacity. In this post, we will explore the essential practices for farm dam maintenance to help farmers maximize the lifespan of their dams and ensure a sustainable water supply.
Regular Inspections:
Regular inspections are the cornerstone of effective farm dam maintenance. Inspecting the dam periodically allows you to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Look for signs of erosion, leaks, cracks, or any unusual structural changes. Additionally, inspect the surrounding areas for any signs of erosion that could compromise the integrity of the dam. These inspections should be conducted at least twice a year, with more frequent checks during periods of heavy rainfall or drought.
Vegetation Management:
Vegetation around and within the dam can cause significant damage if not properly managed. Tree roots can penetrate the dam walls, leading to leaks and structural instability. Regularly trim and remove trees, shrubs, and other vegetation around the dam to prevent such issues. Additionally, control the growth of aquatic plants within the dam to maintain water flow and prevent excessive nutrient buildup.
Sediment Removal:
Sediment buildup is a common issue in farm dams, particularly in areas with high soil erosion rates. Over time, sediment accumulation can reduce the water storage capacity and affect water quality. Regularly remove sediment from the dam to maintain its efficiency and prolong its lifespan. This can be done through dredging or using sediment traps and silt fences to prevent excessive sedimentation.
Erosion Control:
Erosion is a major threat to the integrity of farm dams. Heavy rain, inadequate runoff management, and poor soil conservation practices can contribute to erosion around the dam walls. Implement erosion control measures, such as constructing terraces, planting erosion-resistant vegetation, and using riprap or gabion walls to protect the dam from erosion. Properly designed spillways and outlet structures can also help manage excess water flow and prevent erosion.
Water Quality Management:
Water quality is paramount for the health of livestock, crops, and overall farm productivity. Regularly monitor the water quality in your dam, especially if it is used for irrigation or livestock consumption. Test for pH levels, dissolved oxygen, nutrient concentrations, and potential contaminants. If necessary, implement measures such as adding lime to adjust pH, aerating the water to increase oxygen levels, or installing sediment filters to improve water quality.
Maintenance of Infrastructure:
Aside from the dam itself, the associated infrastructure, such as pipes, valves, and pumps, also require regular maintenance. Inspect these components for leaks, corrosion, or any signs of damage. Clean and repair as necessary to ensure proper functioning. Maintain a record of repairs and replacements, and schedule regular maintenance tasks to prevent unexpected failures.
Pest Control:
Pests, such as rodents and burrowing animals, can pose a threat to the structural integrity of farm dams. They can dig tunnels that weaken the dam walls and increase the risk of leaks or breaches. Implement pest control measures to deter these animals from damaging the dam. This can include installing fences, traps, or using natural deterrents.
Safety Measures:
Farm dams can present safety hazards, especially for children and livestock. Implement appropriate safety measures, such as fencing around the dam, signage indicating potential risks, and education for farm workers and family members about the dangers associated with dams. Regularly inspect safety features and ensure they are in good working condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, farm dam maintenance is essential for their longevity and reliable functionality. Regular inspections, vegetation management, sediment removal, erosion control, water quality management, infrastructure maintenance, pest control, and safety measures are all critical practices for ensuring the longevity of farm dams. By incorporating these practices into a routine maintenance schedule, farmers can safeguard their water supply, protect their agricultural investments, and contribute to sustainable farming practices for years to come